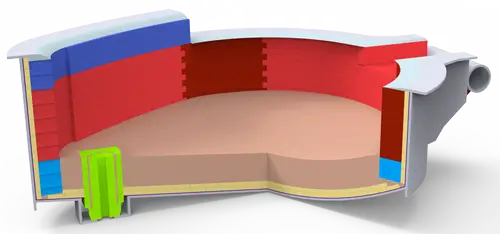
Refractory materials are referred to as refractory materials. Generally, they are made of inorganic non-metallic materials with a refractoriness of more than 1580℃. They can withstand the physical and chemical effects of gases, dust, slag, liquid metal and other substances, and have a certain strength of masonry and knotting performance. If the refractory materials are crushed, ground, screened, and mixed, and a small amount of additives that are both lubricants and adhesives are used to mix, pressed into shape, dried, calcined or melted to obtain products, they are called refractory products.
1.Refractory products In electric furnace steelmaking, refractory products are mainly used for ladle and pouring system, electric furnace lining and steel spout. Due to different parts and working conditions, the requirements for the performance of refractory products are also different, that is, different parts should use different refractory products.
2.Knotted refractory materials for furnace lining Knotted refractory materials for basic furnace lining are mainly magnesia and dolomite. Magnesia is made from natural magnesite (MgCO3) after high temperature roasting at 1650℃. When the roasting temperature is 650℃-690℃, magnesite decomposes.
MgCO3→MgO+CO2
At this time, MgO will absorb moisture and produce Mg(OH)2 when stored in the air for a long time, and cannot be used as a refractory material. Increasing the roasting temperature to above 1550℃ can solve the water absorption problem of magnesia. At this time, magnesia is called sintered magnesia or metallurgical magnesia.
Dolomite is made from natural dolomite ore (CaCO3 MgCO3) after high temperature roasting. Its main components are magnesium oxide and calcium oxide. When the roasting temperature reaches 700℃-900℃, the dolomite ore undergoes the following reactions:
CaCO3 MgCO3→MgO+CaO+2CO2
At this time, the dolomite has a strong ability to absorb water and CO2. After being roasted at a high temperature of 1500℃~1700℃, the water absorption rate of the dolomite slows down. If iron oxide scale is added during roasting to make it generate calcium ferrite with calcium oxide, or a layer of coal tar or paraffin is applied to the roasted dolomite sand to prevent it from breaking and pulverizing, it can be kept for about 10 days and can be used as a refractory material for steelmaking.
Refractory Clay
In metallurgy, except for the masonry of high-aluminum products containing 48%-55% Al2O3, which can be replaced by clay refractory mud of grade NF-40, the masonry, padding and caulking of general refractory products all require homogeneous refractory mud to avoid mutual corrosion at high temperatures, and require high refractoriness and a certain ability to resist high temperatures. The refractory mud commonly used in electric furnace steelmaking includes four types: clay, high-aluminum, magnesium, and silicon. When used, they are mixed with binders and prepared at any time. When high-aluminum refractory mud is used for masonry of high-aluminum bricks, in order to prevent high-temperature shrinkage, an appropriate amount of clinker should be added to the mud. Clinker is made by calcining high-aluminum bauxite, or it can be made of powder ground from crushed waste high-aluminum bricks. Raw material is made of soft clay, and its function is to give the refractory mud a certain bonding ability. When laying silica bricks with silica refractory mud, in order to increase the viscosity of the silica refractory mud, a small amount (<15%) of soft clay can be added, but the amount should not be too much, so as not to reduce the refractoriness. Magnesia-chrome bricks are generally dry-laid, because wet-laid bricks will cause them to pulverize at high temperatures.

More details about EAF Furnace
What does EAF mean on a furnace?
An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats material by means of an electric arc. An electric arc furnace (the large cylinder) being tapped Rendering of exterior and interior of an electric arc furnace.
What is the difference between EAF and BOF furnace?
The Difference Between EAF and Blast Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) While EAF steelmaking relies on electricity and recycled metals, Blast Furnace/BOF depends on raw materials like Iron Ore and Metallurgical Coke as part of a process where oxygen is blown into the furnace at a high velocity.
What is the difference between EAF and induction furnace?
The primary difference between induction furnace and electric arc furnace is in their heating principle i.e., an induction furnace generates heat through electromagnetic induction, whereas an electric arc furnace produces heat by creating an electric arc between two electrodes.
Do electric arc furnaces use coke?
Unlike conventional steelmaking processes such as the blast furnace method, which relies on coke and iron ore, EAFs primarily rely on recycled scrap metal, making them environmentally friendly and reducing reliance on raw materials.