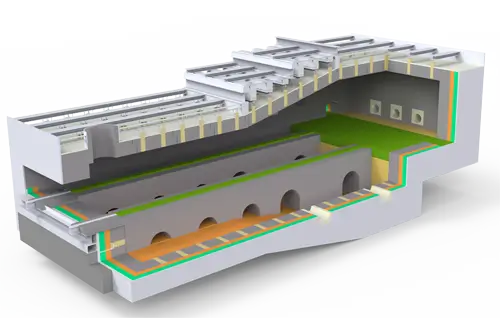
Industrial heating furnaces are widely used in industries such as metallurgy, petroleum, and chemicals to heat metal materials to temperatures suitable for rolling and forging. The article details the key structures of industrial heating furnaces, including the radiation chamber, convection chamber, waste heat recovery system, burner, and ventilation system. The radiation chamber primarily heats the material through radiant heat, while the convection chamber transfers heat through flue gas convection. The waste heat recovery system recovers waste heat, the burner is responsible for fuel combustion, and the ventilation system ensures air flow and flue gas emissions. The operating principle of an industrial heating furnace is based on the high-temperature flame and flue gas generated by fuel combustion. Heat is transferred to the medium within the furnace tubes through radiation and convection, bringing it to the required process temperature.
Industrial heating furnaces are widely used in the metallurgical industry. Their primary function is to heat metal materials to temperatures suitable for rolling and forging. Currently, they are used in a wide range of industries, including petroleum, metallurgy, and chemicals.
There are many different types of industrial heating furnaces, each with its own distinct structure and operating principles. Common types include tubular heating furnaces, vertical heating furnaces, and horizontal rotary reactors.
Structure of industrial heating furnace
1.Radiation Room
The radiation chamber is the primary location for heat exchange within the heating furnace, accounting for approximately 70%-80% of the total furnace heat load. The reaction and cracking processes in hydrocarbon steam reformers and ethylene crackers are all carried out in the radiation chamber. The furnace tubes in the radiation chamber transfer heat via flame or high-temperature flue gas, primarily through radiation, hence the name “radiant tube.” Directly irradiated by the flame, they reach very high temperatures. Therefore, the material used must possess sufficient high-temperature strength and chemical stability.
2.Convection Chamber
The convection chamber heats the material by convection heat transfer from the high-temperature flue gas discharged from the radiation chamber. The flue gas washes the tube wall of the furnace tube at a relatively high speed, and conducts effective convection heat transfer. Its heat load accounts for about 20%-30% of the entire furnace. The convection chamber is generally arranged above the radiation chamber, and some are placed separately on the ground. In order to improve the heat transfer effect, the furnace tube often uses nail head tubes or fin tubes.
3.Waste heat recovery system
Waste heat recovery systems are used to recover waste heat from heating furnaces. There are two methods: one involves preheating the combustion air, returning the recovered heat to the furnace. The other involves using a separate heat recovery system. The former is known as the air preheating method, while the latter is often referred to as the waste heat boiler water recovery method.
4.Burner
The burner’s function is to burn the fuel and provide heat for heat exchange. It consists of a fuel nozzle, an air distributor, and a combustion channel. Burners are categorized as oil burners, gas burners, and combination oil and gas burners, depending on the fuel used. Burner performance directly impacts combustion quality and the furnace’s thermal efficiency.
5.Ventilation System
The function of the ventilation system is to guide the combustion air into the burner and lead the exhaust smoke out of the furnace. It is divided into two ways: natural ventilation and forced ventilation. The former relies on the suction of the chimney itself, and the latter uses a fan.
With professional technology, our company provides a variety of industrial heating furnaces, and we are also one of the manufacturers of laboratory hot air furnaces.
Working principle of industrial heating oven
- First, the high-temperature flame and flue gas generated by the combustion of fuel in the furnace serve as heat sources to heat the medium flowing within the furnace tubes, bringing them to the specified process temperature.
- Next, fuel is injected from the burner and combusted, generating a high-temperature flame and flue gas. The high-temperature flame transfers heat through radiation to the furnace tubes in the radiation chamber, and then to the medium within the tubes.
- The high-temperature flue gas, drawn upward by the chimney or the induced draft fan, enters the convection chamber of the heating furnace, where it transfers heat through convection to the furnace tubes in the convection chamber and then to the medium within the tubes.